Have you ever wondered how search engines organize the endless web pages you browse or how retailers monitor every twist in market trends? Picture yourself as a digital detective, tasked with uncovering hidden patterns and extracting valuable information from the sprawling World Wide Web.
The secret to mastering this world lies in understanding web scraping vs crawling. Many confuse these two essential techniques, but knowing the distinction can transform how you collect data, optimize your web projects, and gain a true edge over competitors.
In this guide, we demystify the entire crawling process, reveal expert tactics for extracting data from target websites, and show you how to turn unstructured data into high-quality intelligence. Unlock the power of web scraping vs crawling and become the strategist who truly understands how to turn information online into real business assets.
The Critical Pre-Flight Check: Data Before You Scrape
Before deploying web scraper tools or automated scripts, the first strategic move for gathering data is to check for better data sources. The 80/20 rule in web data extraction applies:
Do not code a custom web scraper if an official API already exists. This initial check for structured data alternatives will save immense resources and time scraping data.
Public & Private APIs: The Official Door
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) often allow the automated process of collecting data directly from a web page or multiple websites.
- Features: APIs provide structured data and web data that are clean, legal, and often have less risk of scraping legal issues. They enable efficient retrieval and are low-maintenance because website owners manage them.
- When to Use: Ideal for e-commerce, retail marketing, search engine results pages, and social media platforms with available official APIs or paid access.
Commercial Data Vendors: The Ready-Made Dataset
Some vendors handle the entire pipeline for you, offering data crawling, business data scraping, and validated, extracted data in a structured format.
- Features: Ready-made datasets include web data collected by commercial web crawlers and scrapers, often targeting market research, competitor monitoring, or market trends analysis.
- When to Use: Market research, trend analysis, collecting high-quality data from review sites, or when you require sentiment analysis across a wide scope.
Webhooks & RSS Feeds: The Subscription Model
Webhooks and RSS feeds provide automated notification the moment new information online becomes available, often as part of web indexing.
- Features: Event-driven, low-latency, and optimal for keeping your data up to date.
- How They Work: These tools help index pages passively, pushing only new or updated content, reducing the need to crawl data unnecessarily.
The Dual Engines of Web Data: Function and Form

If there are no available APIs or vendors, it is time to understand your tools: web crawlers and web scrapers. In web scraping vs crawling, you need to know that crawling is discovering all the pages on the World Wide Web, whereas web scraping targets extracting information from a specific web page.
Web Crawling: The Discovery Engine
Web crawling is the systematic process that web crawlers (also called spider bots) use to index web pages by following web links. Automated scripts and web crawler tools traverse seed URLs, finding new links, indexing web pages, and building a map of site structure.
- Key Feature: Distributed spider bots manage a prioritized queue of web pages (URL Frontier). This is how search engines like Google build their search engine results pages.
- Why It Is Important: Crawling enables automated scripts to index all the pages of the World Wide Web, supporting website data discovery, technical SEO, and data collection for search engine optimization.
Web Scraping: The Extraction Refinery
Web scraping refers to using a web scraper to extract data from a target website or multiple websites and convert unstructured data into a structured format like JSON or CSV.
While crawling is about discovering URLs and new links, scraping is about extracting data based on CSS selectors, XPath, or custom parsing for specific data.
- Key Feature: Web scrapers use surgical methods, navigating the HTML structure of a web page to extract the desired data fields, such as prices, reviews, or business data scraping output.
- Why It Is Important: Scraping transforms chaotic, unstructured data into valuable website data, enabling insight generation for market research, retail marketing, and automated business decision-making.
The Core Difference: A Side-by-Side Comparison
To highlight the essential difference in web scraping vs crawling, review the table below comparing both processes:
| Aspect | Web Crawling (Discovery) | Web Scraping (Extraction) |
| Primary Action | Indexing & Link Following | Targeted Data Parsing & Filtering |
| Scope | Broad, Exploratory (all the pages) | Narrow, Surgical (extract specific data) |
| Goal | Discover and map web links and web page connections | Collect relevant information and desired data |
| Data Focus | Deduplication, crawling processes, and data freshness | Precision, schema validation, structured format |
| Output | List of URLs, HTML dumps, web indexing | Structured datasets (JSON, CSV, Database), extracted data |
Strategic Requirements and Optimization
Knowing the difference is just the start. The real value comes from optimizing your crawling process and scraping process for efficient, scalable data collection.
For instance, in retail marketing, you can crawl data from thousands of competitor web pages, extracting data such as current prices using web scraping tools for dynamic price optimization.
For market research, data crawling identifies all the pages to monitor, while business data scraping targets the specific data needed from those web pages.
Key Functional & Non-Functional Requirements
To ensure the automated process delivers high-quality data, certain requirements must always be met:
- Functional (Mandatory): The web crawler must respect robots.txt, avoid IP blocks, deduplicate URLs, render JavaScript when needed, and handle automated process error management.
- Non-Functional (Improvement): Build scalable, fault-tolerant, and resilient data extraction systems to keep extracted data up to date, even as target websites change.
Top Secret Techniques: The Insider’s Playbook
Advanced anti-bot countermeasures make scraping projects more challenging. Mastering these web scraping legal and technical hurdles is key to gathering data at scale from target websites.
Win the Anti-Bot War
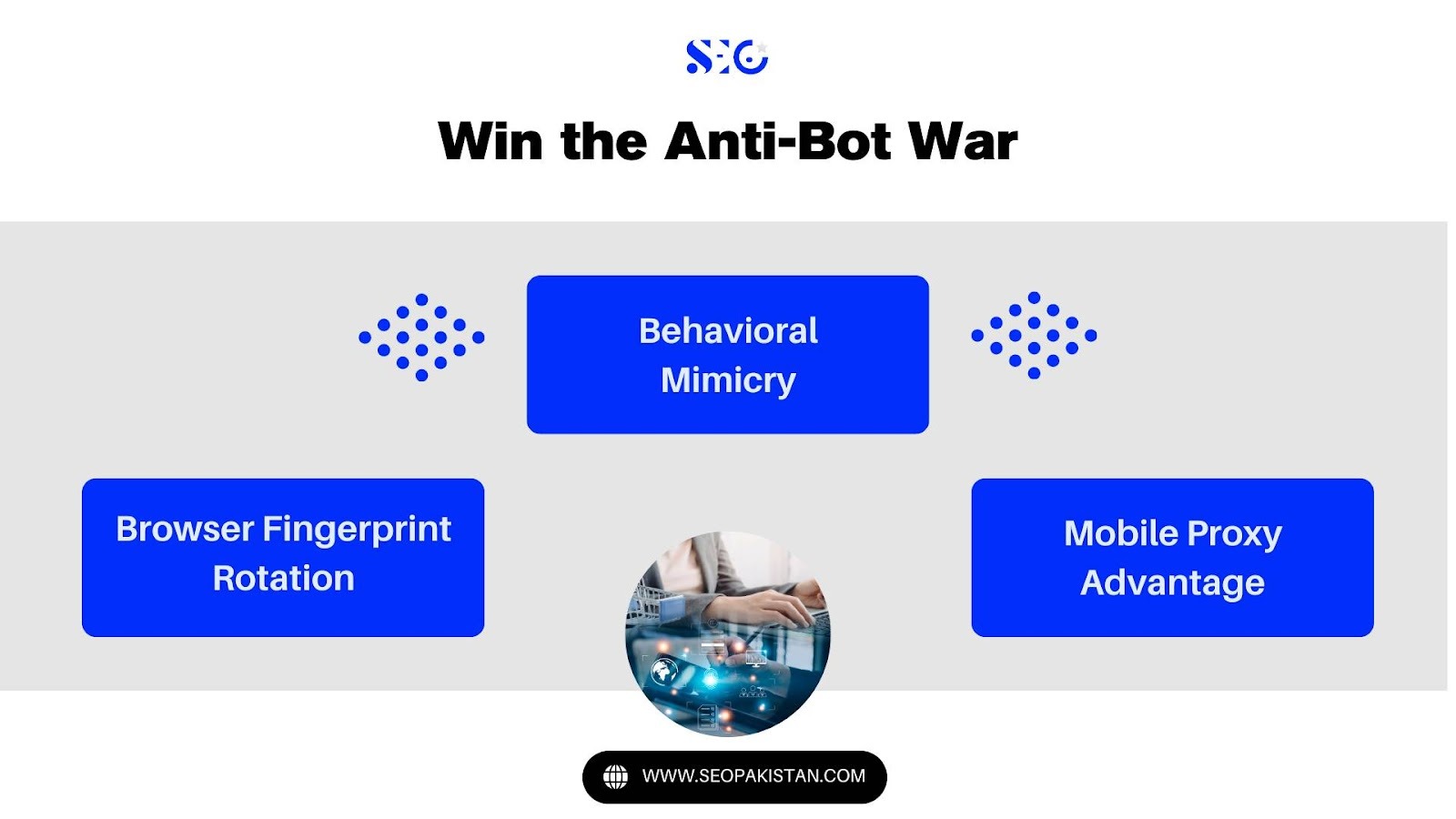
- Behavioral Mimicry: Automated process scripts should simulate human mouse movements, scroll depth, and random delay patterns to avoid detection by website owners using User Behavior Analysis.
- Browser Fingerprint Rotation: Rotate HTTP headers, user agent strings, and use multiple browser instances to bypass web scraper and device fingerprint detection.
- Mobile Proxy Advantage: Crawl and scrape data using 3G, 4G, or 5G proxies to access the same target website as real users, avoiding blocks and enabling continuous data collection.
The Data Quality Secret: Schema Validation
Schema validation ensures each scraping project delivers only high-quality, structured data. If necessary data, such as price or title field, is missing, the system should flag the web page for immediate re-scraping, ensuring complete, usable extracted data for your business.
7 Benefits of a Strategic Data Pipeline
When you unify web crawling work and the scraping process using automated scripts and web crawler tools, you unlock extraordinary business potential:
- Competitive Edge: Real-time, localized pricing intelligence from multiple websites.
- Risk Mitigation: Automated scripts monitor news, regulatory, and review sites for risk signals.
- Predictive Analytics: Gather data to build clean datasets for forecasting market trends.
- Cost Efficiency: Well-optimized crawling process reduces bandwidth and server loads.
- Technical SEO Mastery: Instantly detect broken links, duplicate pages, and unauthorized changes.
- Superior Customer Insights: Web scraping allows for collecting data from thousands of reviews, supporting rapid sentiment analysis and feature improvement.
- High-Availability Compliance: Fault-tolerant architectures for web scraping tools ensure your data pipeline never fails silently.
Conclusion:
Web scraping vs crawling is a dual process: web crawling discovers all the web pages, and web scraping extracts the necessary data from them. Treating these as the same process will limit your ability to collect data, extract data, and turn unstructured data from the web into actionable, high-quality data assets.
It is no longer about merely browsing or indexing web pages. The automated process now requires orchestrating a stealthy, scalable, and intelligent pipeline, one that collects relevant information from the World Wide Web using web crawlers and extracts business value using advanced web scraping tools.
Start thinking like an insider data strategist to build reliable, compliant, and efficient web data extraction systems that deliver genuine business growth with seo pakistan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a crawler in web scraping?
A crawler, also called a web spider, systematically browses the web to discover and index URLs for further processing, such as scraping.
What is another name for web scraping?
Web scraping is also called data scraping or web harvesting.
What is the difference between a web crawler and a web browser?
- Web crawler: Automates discovering and indexing web pages.
- Web browser: A tool for humans to visually interact with and navigate websites.
What is the difference between web scraping and data scraping?
- Web scraping: Extracts data specifically from websites.
- Data scraping: Broader term; extracts data from any source, not just the web.
What is the difference between crawling and scraping?
- Crawling: Discovers and indexes web pages (discovery).
- Scraping: Extracts specific data from web pages (extraction).