Ever wondered what invisible visitor constantly explores your website, determining whether your content deserves to appear in Google search results? The answer lies in understanding Google’s sophisticated web crawling system.
Google uses a web crawler called Googlebot to discover, analyze, and index web pages across the internet. This automated program serves as Google’s digital scout, methodically visiting websites to understand their content and structure. Without Googlebot’s continuous work, your website would remain invisible to the billions of people searching Google every day.
But here’s what most website owners don’t realize: Googlebot isn’t just one crawler. It’s actually a family of specialized bots, each designed for specific tasks. Understanding how these crawlers work and how to manage them can dramatically impact your website’s search engine performance.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about Google’s web crawlers, from their technical processes to practical management strategies that put you in control of your SEO destiny.
The Direct Answer: The One-and-Only Googlebot
Googlebot is the main web crawler used by Google, a tool that automatically scans websites to find new content and track updates on existing pages.
Think of it as Google’s tireless digital librarian, constantly cataloging the ever-expanding internet.
When you check your website’s server logs, Googlebot appears as the most frequent visitor. Its user agent string identifies it clearly, making it easy to spot among your regular human visitors. This crawler operates 24/7, following links from page to page and building Google’s comprehensive map of the web.
Googlebot’s fundamental mission is simple yet crucial: find content, understand it, and report back to Google’s indexing systems. Every piece of content that appears in Google search results has been discovered and analyzed by this crawler first.
The crawler doesn’t simply visit your site once and move on. Googlebot returns regularly to check for updates, new pages, and changes to existing content. This ongoing oversight helps keep Google’s search results updated and accurate.
It’s Not Just One: The Family of Googlebots
What many don’t realize is that “Googlebot” actually represents multiple specialized crawlers working together. Each serves a distinct purpose in Google’s content discovery ecosystem.
Here are the key members of the Googlebot family you should know:
- Googlebot Smartphone serves as Google’s main crawler. Since Google switched to mobile-first indexing, this bot crawls your website as if it were a smartphone user. It evaluates your mobile experience first, making mobile optimization absolutely critical for search visibility.
- Googlebot Desktop serves as the secondary crawler, focusing on desktop-specific content and experiences. While less prioritized than its mobile counterpart, it still plays an important role in understanding how your site performs across different devices.
- Googlebot Image and Googlebot Video focus on finding and processing multimedia content. These crawlers help your images and videos appear in Google’s specialized search results, opening additional traffic opportunities.
- AdsBot reviews landing pages for Google Ads campaigns to ensure your advertising destinations comply with quality standards.
- GoogleBot News focuses specifically on news content, helping publishers get their articles into Google News results.
Each crawler has slightly different behaviors and priorities, but they all follow the same fundamental rules you set through robots.txt files and meta tags.
How Does a Web Crawler Work? The Process of Discovery
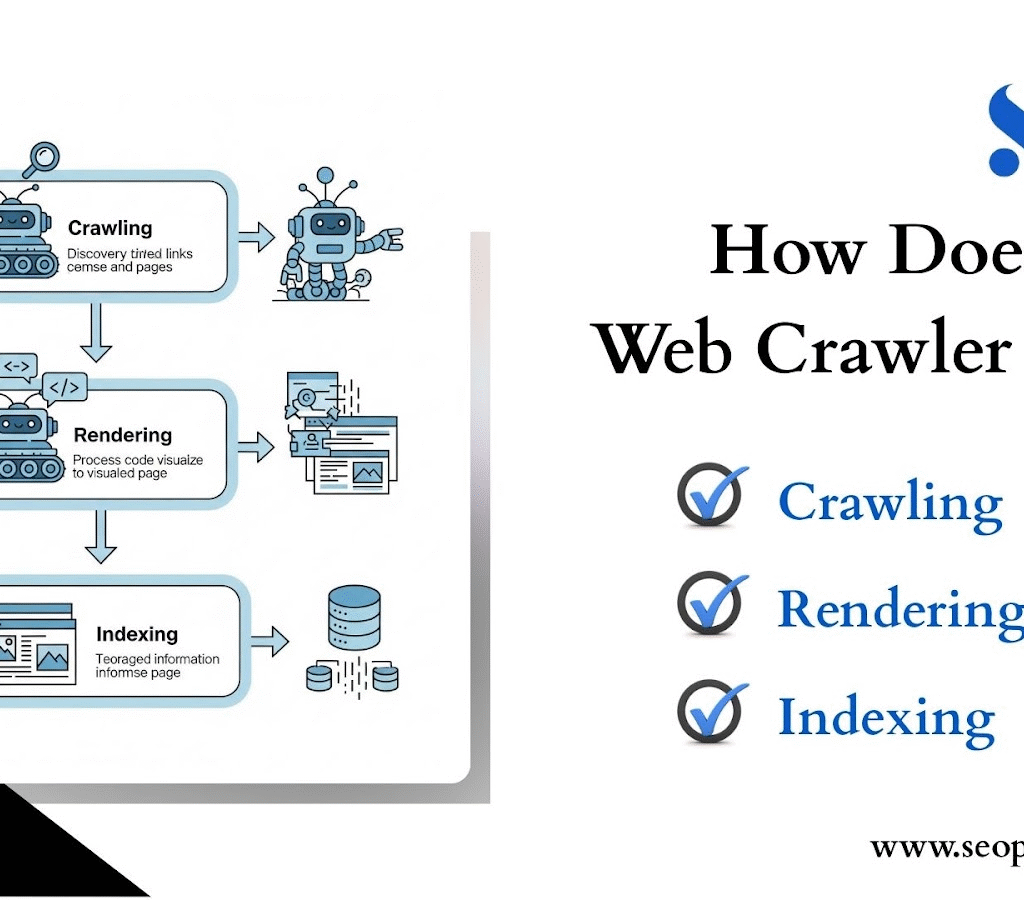
Understanding Googlebot’s process helps you optimize your website for better search performance. The crawler follows a systematic three-step approach that transforms raw web pages into searchable content.
Step 1: Crawling
- Googlebot discovers new URLs through multiple pathways. It follows links from previously crawled pages, reads XML sitemaps you’ve submitted, and explores URLs suggested by Google Search Console.
- The crawler maintains a massive queue of URLs to visit, prioritizing based on factors like site authority, update frequency, and content importance.
- At this stage, Googlebot follows the guidelines set in your robots.txt file. If you’ve blocked certain sections of your site, the crawler will skip them entirely.
- This crawling stage determines which pages Google even considers for inclusion in search results.
Step 2: Rendering
- Once Googlebot accesses a page, it processes all the code—HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to render the page as a human visitor would see it.
- Modern Googlebot can execute JavaScript and wait for content to load, making it capable of crawling single-page applications and dynamically generated content.
- However, pages that load slowly or require complex user interactions may not render completely.
Step 3: Indexing
After rendering, Googlebot analyzes the page content and sends relevant information back to Google’s indexing systems. Google’s algorithms evaluate the content’s quality, relevance, and relationship to other pages on your site.
Not every crawled page gets indexed. Google may choose to exclude pages due to quality issues, duplicate content, or specific directives like noindex tags.
Taking Control: How to Manage Googlebot on Your Site
Smart website owners don’t just wait for Googlebot to visit, they actively manage how the crawler interacts with their content. Two primary tools give you this control.
Robots.txt File
Your robots.txt file acts as a gatekeeper, telling crawlers which parts of your site they’re allowed to explore. This plain text file sits in your website’s root directory and provides crawling instructions to all search engine bots.
Use robots.txt to block crawlers from accessing admin areas, duplicate content, or resource-heavy pages that don’t need indexing. However, remember that robots.txt only prevents crawling; it doesn’t guarantee pages won’t appear in search results if other sites link to them.
Noindex Tag
The noindex meta tag provides more granular control by telling Google not to include specific pages in search results, even if they’ve been crawled. This tag is perfect for pages that users need to access but shouldn’t appear in search results, like thank-you pages or internal tools.
Here’s a helpful comparison to clarify when to use each tool:
| Feature | robots.txt | noindex tag |
| Purpose | Prevents crawling | Prevents indexing |
| Best for | Blocking large sections | Blocking specific pages |
| Function | Tells the crawler “Don’t go here” | Tells Google “Don’t show this” |
Understanding this distinction helps you implement the right solution for your specific needs. Pages blocked by robots.txt won’t be crawled at all, while pages with noindex tags will be crawled but excluded from search results.
Beyond Googlebot: The World of Search Engine Crawlers
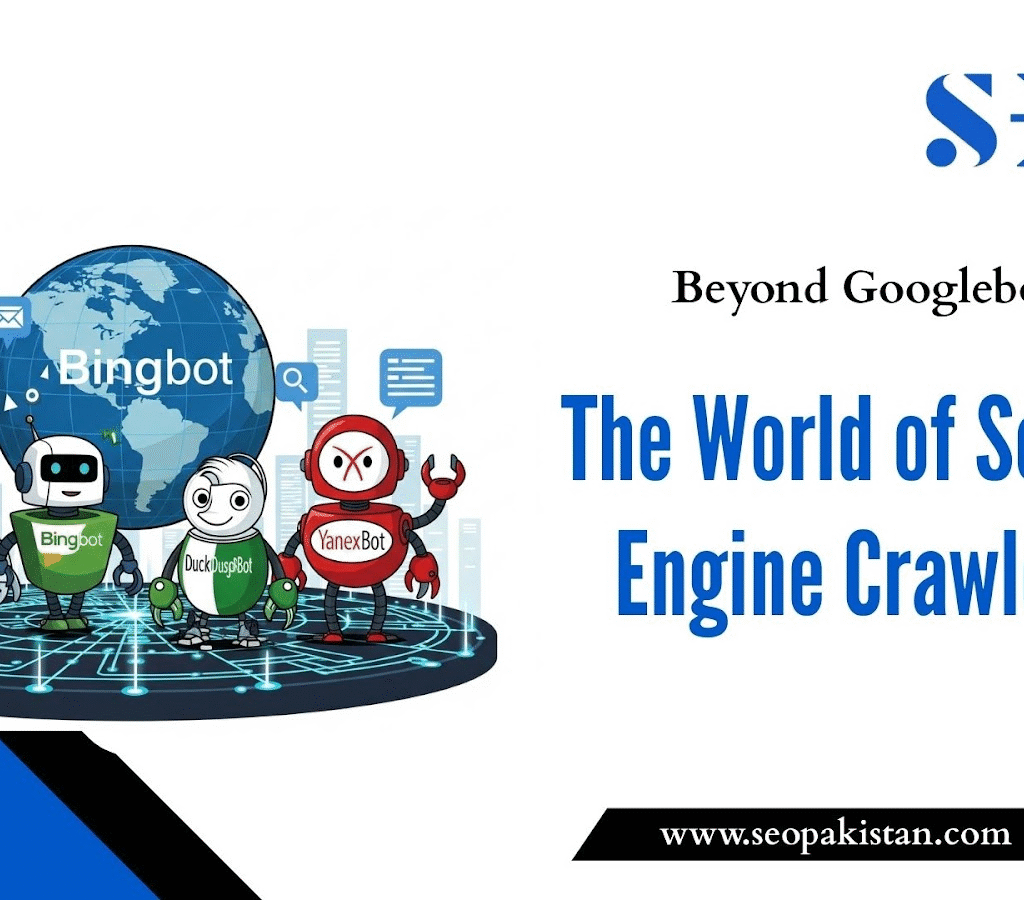
While Googlebot dominates the web crawling landscape, other search engines deploy their own crawlers that may visit your website. Understanding these additional bots helps you optimize for search engines beyond Google.
Bingbot is the web crawler developed by Microsoft, responsible for indexing content for the Bing search engine. While Bing holds a smaller market share than Google, it still drives significant traffic, especially for certain demographics and regions.
DuckDuckBot is the web crawler used by DuckDuckGo, a search engine dedicated to privacy. This crawler tends to be more respectful of bandwidth limitations and crawls less aggressively than larger search engines.
YandexBot serves as the primary crawler for Yandex, Russia’s dominant search engine. For effective regional SEO with Russian-speaking audiences, it’s essential to understand how YandexBot operates.
Each crawler has unique characteristics and crawling patterns, but the fundamental principles remain consistent. Respectful crawling practices, clear robots.txt instructions, and quality content appeal to all search engine crawlers.
Most website management tools and analytics platforms can help you identify which crawlers visit your site and how frequently they return.
Conclusion
Mastering Googlebot’s behavior and preferences forms the foundation of successful search engine optimization. Every SEO strategy ultimately depends on how well search engine crawlers can discover, understand, and index your content.
When you optimize for Googlebot, you’re essentially optimizing for the world’s most popular search engine. This means more potential visitors, better search rankings, and increased online visibility for your brand or business.
The websites that perform best in search results aren’t just lucky; they understand how crawlers work and design their content accordingly. They make strategic decisions about site structure, loading speed, and content organization based on crawler behavior.
By taking control of how Googlebot interacts with your website, you’re positioning yourself to succeed in the competitive world of search engine rankings. The knowledge you’ve gained here puts you ahead of countless website owners who never think about the invisible visitors that determine their online success.
Ready to dominate the search rankings? Head over to SEOPakistan.com and supercharge your online presence now!
Frequently Asked Question
What is the primary purpose of Googlebot?
Googlebot is Google’s main web crawler, an automated program that discovers new content and updates to existing pages across the internet. Its fundamental mission is to find and understand content and then report back to Google’s indexing systems so that the pages can appear in search results.
Is Googlebot just one single crawler?
No, “Googlebot” is a general name that represents a family of specialized crawlers, each with a distinct purpose in Google’s ecosystem. For instance, Googlebot Smartphone is the primary crawler for mobile-first indexing, while Googlebot Image and Googlebot Video specialize in multimedia content.
How do web crawlers discover new pages?
Web crawlers like Googlebot discover new URLs by following links from pages that have already been crawled, reading XML sitemaps, and exploring URLs suggested in Google Search Console.
What is the difference between robots.txt and a noindex tag?
The robots.txt file acts as a gatekeeper that tells crawlers which parts of your site they are allowed to explore, preventing crawling of certain pages or sections.